17 Facts About Global Warming
At a time when all hands need to be on deck to fight climate change, it is imperative that you know the important facts about global warming.

Our use of fossil fuels over the last few decades has led to a profound deterioration of our environment. It is the reason why we are dealing with the extinction of wildlife species, the depletion of the ozone layer, and climate change. Unfortunately, even with the best efforts of climate scientists around the world, we are still not doing enough to reverse the damage done to the environment.
What Is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the increase in the average surface temperature of the earth and oceans. The increase stems from the fact that human activity has increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, trapping more heat than necessary within the earth. Global warming has worsened significantly since the year 2000 as all but one of the 16 hottest years since NASA started keeping records, have occurred since the turn of the millennium.
What Is the Difference Between Global Warming and Climate Change?
It is common to find people using global warming and climate change interchangeably, but they don’t mean the same thing. Climate change refers to all the complex changes in the earth’s climate system—including global warming. It covers all other extreme weather conditions, rising seas, changes in wildlife constituencies, and more. So if climate change is a disease, global warming is one of the numerous symptoms.
What Causes Global Warming?
Global warming is caused by air pollutants and greenhouse gases (including carbon dioxide) combining to trap the sunlight and solar radiation bouncing off the earth’s surface. Usually, most of the radiation finds its way back into space, but the pollutants keep the heat in, forcing the earth to get warmer. Unfortunately, the gases we send into the air can remain active for years or even centuries. This is why the fight against global warming cannot be looked at from a short term angle.
Around the world, burning of fossil fuels to generate electricity and aid in transportation are some of the biggest contributors of heat-trapping pollutants into the atmosphere (including multi-billion tons of CO2 per year).
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
The earth is habitable because the greenhouse effect warms up the earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy hits the earth’s surface, most of it is reflected back to space while the remainder is absorbed and redistributed by greenhouse gases.
Some of these gases include carbon dioxide, water vapor, ozone, nitrous oxide, methane and artificial gases like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). The absorbed energy keeps the earth’s temperature 33 degrees warmer than it would have been without this phenomenon, hence allowing life to flourish on earth.
However, with the rise in human activity since the industrial revolution, activities such as large scale agriculture, fossil fuel burning, land clearing and more, have led to an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. With a thicker concentration, the gases are trapping more sun radiation than we really need hence leading to the warming of the earth.
The problem we now face is that human activities – particularly burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), agriculture and land clearing – are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases. This is the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is contributing to the warming of the Earth.
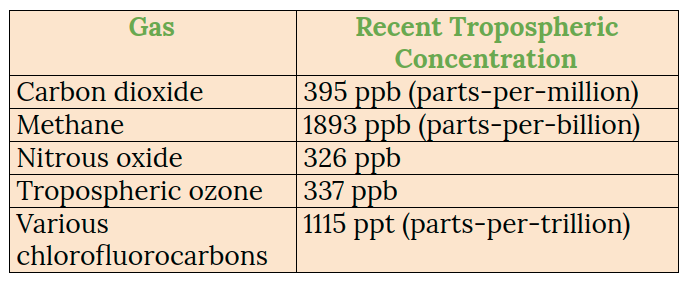
Summary Table of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere today are summarized in the table below:
17 Facts about Global Warming
At a time when all hands need to be on deck to fight global warming, it is important that you know the important facts. Here are 17 of them:
- Global warming is happening due to the excess emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, as a result of human activities. The gases can remain in the atmosphere for many years, making the fight against global warming a long-term one.
- We are emitting more carbon dioxide at a level that is overwhelming for the plants and oceans.
- There is more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today than at any point over the last 800,000 years.
- America makes up 4% of the world’s population, but it is responsible for 25% of the historical carbon dioxide pollution from fossil-fuel burning.
- By the end of this century, sea levels will rise by 7-23 inches due to global warming. They’ve risen by 7 inches in the last century alone, which is more than the previous 2000 years combined. In the U.S. alone, 13 million people could be forced to relocate due to sea-level rise by the year 2100.
- The average temperature around the world has steadily increased since 1880. By the year 2100, the average temperature will rise by up to 3.1 degrees Celsius.
- The Arctic is one of the regions hardest hit by global warming as the average temperature has risen at twice the global average. The ice in the region is melting rapidly, with ice-free summers in the area expected as early as 2040.
- The last decade was the hottest since records began in the last 140 years.
- In 1850, there were 150 glaciers in the Montana Glacier National Park, but today, there are only 25. The melting of glaciers is responsible for the rise in sea levels, and it is also responsible for freshwater shortages in places that are reliant on natural water sources.
- Today, coral reef bleaching is at its highest level since 1980 as a result of global warming and pollution.
- Due to the impact of global warming on the earth’s weather system, heat waves, tropical storms and forest fires are now more common.
- Disappearing habitats due to climate change have put more than 1 million species at risk of becoming extinct. 680 species with backbones and 559 domesticated breeds of mammals used for food have already gone extinct since 1600.
- Some impacts of climate change could be irreversible by 2030.
- Between 2000 and 2100, heat-related deaths could rise by around 150,000.
- As colder regions become hotter as a result of global warming, the inhabitants of these regions are becoming more vulnerable to diseases.
- The years 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018 had the highest temperatures since 1880 and according to WMO, the long-term trend is an upward one.
- Global warming can lead to intense food shortages around the world.
How Is Global Warming Linked to Extreme Weather?
After decades of work, scientists have found a link between global warming and extreme weather.
Heat and drought
The dangers of heatwaves are more pronounced in the presence of extreme temperature and humidity, especially when the conditions persist for more than two days. As we keep seeing new temperature highs every year, it is very likely that anthropogenic global warming is making heat-related events more frequent.
Storms and floods
More evaporation (as a result of heat) leads to higher moisture content in the atmosphere. So clouds that can release heavy rains thrive in warmer temperatures. This is why the rainfall during Hurricane Harvey was 15% more intense than it should have been without human-induced global warming.
As temperatures continue to soar, categories 4 and 5 storms will become more common. Scientists are yet to establish the relationship between global warming and more hurricanes, but they know that rising sea levels are causing higher storm surges and more floods. Interestingly, around half of the sea-level rise seen since 1900 can be traced to human-global warming.
Record snowfall
Due to more moisture in warmer temperatures, snowfall records are created around the world during the winter, with more regularity. The rapidly warming Arctic weakens the jet stream which allows cold polar air to spread southwards triggering heavy snow.
What Are the Other Effects of Global Warming?
Scientists around the globe have documented many environmental, economic, and health consequences of global warming. Some of these include the following:
- Dramatic water shortages can increase the risk of wildfires that can cause billions in lost work- hours and revenue around the world.
- Rising sea levels are making tourist destinations around coastal cities less attractive, and many of them will get submerged in the near future.
- Farmers are currently facing the combined threats of heavy downpours over short periods, heat waves, and damage caused by pests seeking new habitats. Agriculture and aquaculture will become more difficult in the coming decades leading to a global food crisis.
- Allergies, asthma and infectious disease outbreaks are now more common and will be harder to manage due to higher levels of air pollution, as well as the spread of conditions that are favorable to known vectors and pathogens.
Global Temperature Trajectories to 2100
According to scientists, the world will continue to warm until the new century and beyond. The conclusion is based on computer simulations designed to deliver projections about the earth’s climate. According to several such simulations, the world will be 1.1 to 5.4°C warmer in 2100. The exact level of warming to be seen is dependent on the actions we take today to cut down greenhouse gas emissions—especially as it concerns the burning of fossil fuels.
Global Warming and Public Policy
Without relevant scientific and socioeconomic data, it is difficult to create public policy on global warming. This is why the World Meteorological Organization and the United Nations Environment Programme created the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 1988.
This body has been at the forefront of shaping public policy regarding global warming and climate change at large. It is in charge of assessing and summarizing all the scientific, socioeconomic and technical data on climate change. Its findings are published for the consumption of stakeholders around the world.
The reports of the IPCC are the basis of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and Kyoto Protocol treaties. The Paris Agreement is also another example of how the IPCC’s efforts can shape public policy on climate change.
Unfortunately, some governments still disregard these efforts. President Trump, for example, pulled the US federal government out of the Paris Agreement in June 2017.
Politics & Global Warming
Political wrangling on global warming goes beyond the various types of skepticism we have discussed above. It cuts across all facets of the debate, and according to research, some people are questioning the motivations behind climate research and many more are simply towing the general beliefs of the political parties they identify with, on anything concerning climate change.
This is dangerous because most partisan interpretations of climate change research detract from the overall conversation at best, and in worst-case scenarios, create more skeptics.
Global Warming in China
China is the most populous country on earth and the largest culprit when it comes to carbon emissions. If it can accept responsibility and work hard at reducing emissions, it will be a powerful ally in the fight against climate change. The severe smog of 2011 pushed the government to launch a plan targeted at cutting down coal consumption and improving air quality.
However, the trade wars between China and the US and the economic slowdown is triggering relaxation of policies in some regions. Coal consumption picked up again in 2019 as the governments so-called “carbon market” has been significantly downsized. If the lax attitude continues, China will set the world back a few more years in the fight against global warming.
Global Warming in the US
There is no denying the fact that the US has been severely affected by global warming. In recent years, six climate-change-related events have led to a loss of $14 billion in the economy. Between 1901 and 2016, the average national temperatures increased by 1.8°F.
Temperatures are expected to rise by 2.5°F between 2021 and 2050. As this continues, weather-related events currently considered extreme will become normal. This means more drought, forest fires, heatwaves, heavier rains and snows, coastal flooding, hurricanes and more.
Unfortunately, politicians in the US are not doing anywhere near enough to correct the damages of global warming and ensure the country is doing its best to reduce the severity of future predictions. The President’s withdrawal from the Paris Agreement is well documented, and many governors have followed his lead by ignoring the climate change discussions.
Presently, 26 states are working together in the United States Climate Alliance, to stick to the dictates of the Paris Agreement, without federal backing. However, for the US to land a significant punch in the fight against global warming, there must be central leadership guiding the whole country in one direction.
The Best Global Warming Solutions
The best global warming solutions are those that can have a direct impact on the environment by helping to cut down on greenhouse gas emissions. Some of these are covered below.
Plant trees
Deforestation means we can no longer rely on trees to absorb the carbon in the atmosphere. To replenish the forests, we need to plant more trees in tropical rainforests around the world. Strategic tree planting in countries like Brazil, Indonesia, Madagascar, India, and Colombia is important if we are to balance the scales in our favor again.
You don’t need to travel to these countries to plant the trees. Organizations like Treedom make it easy for you to plant your choice of trees in any of these places. In your backyard, however, you should contribute your quota to ensure sustainability deforestation.
Embrace sustainable transportation
Cars and airplanes contribute a great deal to the carbon emissions recorded around the world. Choosing sustainable transportation will, therefore, help the climate a great deal. How can you embrace sustainable transportation?
- Buy climate-friendly cars and use cruise control when driving on longer trips. Also, avoid rapid braking and acceleration as it burns more fuel.
- Choose ride-sharing instead of getting a private ride
- Walk or bike to your destination when you can
Reduce your heating bill
It is easy to use more energy than necessary to keep your home warm during the winter. To avoid this, ensure there are no leakages in your doors and windows as they can allow outside air and lower the temperature of the house. Set your thermostat at the optimum temperature to keep the house warm enough and then reduce this temperature by 7-10 degrees for at least 8 hours a day.
Discourage fossil-dependence by divesting from guilty companies
If enough people liquidate their stock holdings from companies that burn coal and other fossil fuels, the brands will come under pressure to become more environmentally friendly. Not sure how to find out if your stocks are invested in fossil-burning companies? Analyze your holdings here. However, remember that this approach only works if enough people do the same so encourage your friends and family to join you.
Embrace climate-change advocacy
One of the most powerful ways to deal with global warming is to become a strong climate change advocate. As advocacy groups grow and crank up the pressure, more politicians will be forced to enact policies that can help the world get closer to winning the fight against global warming. Some of the things you can also do include:
- Sending emails and letters to political candidates in your area telling them you will vote based on their position on global warming.
- Becoming a volunteer on the campaign trail for candidates that have clear plans for fighting global warming.
- Encouraging friends and family to vote in support of candidates that are not climate change deniers.
Conclusion
Global warming is real. For the world to avert major disasters in the coming decades, we need to take collective action now. Contribute your quota to the fight. Educate as many people around you on the dangers of global warming. Push politicians to take climate change seriously. Without a united effort, we cannot slow nor reverse the damage to our planet.
Augurisk is a risk assessment platform for Climate change, Natural Hazards and Societal Risks. We help people and businesses assess climate risks associated with their properties, so they can better prepare for the future.
